无
无
无
无
| 序号 | 学生 | 所属学院 | 专业 | 年级 | 项目中的分工 | 成员类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
娜木汗 | 动物科技学院 | 动物医学 | 2023 | 虻的分子生物学鉴定 |
|
|
|
刘天贺 | 动物科技学院 | 动物医学(创新人才班) | 2023 | 虻所携带的病原流行病学检测 |
|
|
|
时千惠 | 动物科技学院 | 动物医学 | 2023 | 虻的形态学鉴定 |
|
|
|
冯帅 | 动物科技学院 | 动物医学(创新人才班) | 2023 | 样品采集 |
|
|
|
付辰涛 | 动物科技学院 | 动物医学(创新人才班) | 2023 | 相关因素统计学分析 |
|
| 序号 | 教师姓名 | 所属学院 | 是否企业导师 | 教师类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
邱鸿宇 | 动物科技学院 | 否 |
|
[1]许荣满. 黑龙江省虻类采集[C]/ /医学昆虫调查集刊. 北京:中国人民解放军战士出版 社,1983: 101 - 105.
[2]Moucha J. Horse-flies (Diptera:Tabanidae) of the world synoptic
catalogue[J]. Acta Ent. Mus. Nat. Pragae, Suppl.
[3]Baldacchino F, Desquesnes M, Mihok S, et al. Tabanids: neglected
subjects of research, but important vectors of disease agents[J]! Infect.
Genet. Evol, 2014; 28: 596-615.
[4]陆宝麟, 吴厚永. 中国重要医学昆虫分类与鉴别[M]. 郑州:河南科学技术出版社, 2003
[5] Gonzalez C R. Dasybasis elquiensis, a new species of horse fly from
Northern Chile (Diptera: Tabanidae: Diachlorini)[J]. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz,
2000, 95(5): 629-632.
[6]Morita S I, Bayless K M, Yeates D K. et al. Molecular phylogeny of the horse flies: a framework for renewing
tabanid taxonomy[J]. Systematic Entomology, 2016, 41: 56-72.
[7] Coher E I. Species related to Tabanus basalis Macquart, with the
description of a new species from Nepal[J]. Bull. Brooklyn Ent. Soc, 1962,
107:157-162.
[8]Coher E I. Asian biting fly studies Ⅱ. Tabanidae.species related to
Tabanus birmanicus(Bigot), 1892, with the description of a new species from
Nepal[J]. Pacif. Ins, 1971a, 13(2): 321-323.
[9] Chainey J. Horse-flies, deer-flies and clegs (Tabanidae). In:
Kirk-Sproggs AH, Sinclair BJ (Eds) Manual of Afrotropical Diptera, Nematocerous
Diptera and lower Brachycera[J]. South African National Biodiversity Institute,
Pretoria, 2017 893–913
[10] Coher E I. Asian biting fly studies Ⅲ. Tabanidae species related to
Tabanus caerulescens Macquart, 1838, with the description of a new species from
Nepal[J]. Pacif.Ins, 1971b, 13(2): 325- 328.
[11] Ouchi Y. On some horseflies belonging to the subfamily Pangoniinae
from Eastrn and Northern Corea[J]. Shanghai Sci, Inst. Sect. Ⅲ. 1939, 4:
175-189.
[12] Murdoch W P, Takahasi. The female Tabanidae of Japan, Korea and
Manchuris[J]. Mem. Ent. Soc. Wash, 1969, 6: 230.
[13] Watanabe M. Studies on bionomics of deer fly, Chrysops suavis Loew
(Tabanidae,Diptera)[J]. Jpn. Sanit. Zool, 1968, 19(2): 87-92.
[14] Stekhevn S. Tabanids from Sumatra and Borneo[J]. Tijdschr, Ent, 1932b,
75: 78-8
[15] Philip C B. Further notes on Far Eastern TabanidaeⅦ new Generalized
Oriental species of Unusual Zoogeographic interest[J]. Pan-Pacif. Entomologist,
1980, 56(1): 77-78.
[16] Bogitsh B J, Carter C E, Oeltmann T N. Chapter 18-Arthropods as
Vectors. In B. J. Bogitsh, C. E. Carter, & T. N. Oeltmann (Eds.)[M]. Human
Parasitology (Fifth Edition): Academic Press, 2019;
[17] David T J, William A P. Med Vet Entomol. Saunders Elsevier, St. Louis,
Missouri. 2006.
[18] 何静, 刘增加, 徐宏江.青海省双翅目虻科昆虫研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2016, 27(06): 573- 576.
[19] 刘增加, 石淑珍, 宫占威. 甘肃虻科小志[C]. 甘肃省动物学会学术讨论论文. 2001: 1-7.
[20] 高远. 马五种盅口亚科线虫线粒体全基因组比较与进化分析[D]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2018.
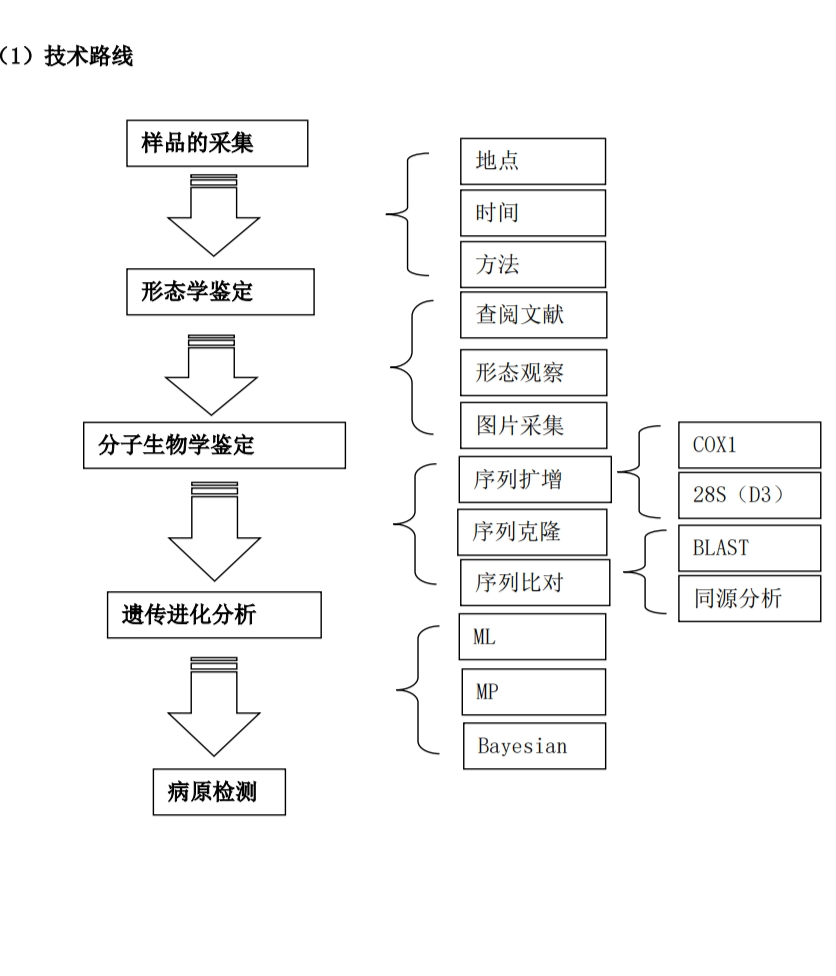
课题组前期已经对大庆市内的主要牛虻进行了形态学鉴定(图 1、图 2)和分子鉴定,应用 引物扩增线粒体 COXI,PCR 结果显示 COXI 约 1500bp(图 3),两种牛虻线粒体基因组的扩增 结果(图 4、图 5),进一步进行测序及进化分析表明这两种虻分别为范式斑虻(Chrysops vanderwulpi)和土耳其麻虻(Haematopota
turkestanica)。
图 1 范式斑虻形态图
A:范式斑虻背侧面;B:范式斑虻腹面;C:范式斑虻头部;
D:范式斑虻头部侧面;E:范式斑虻的翅
Fig. 1 Morphological map of Chrysops
vanderwulpi
A: The dorsal side of Chrysops
vanderwulpi; B: The ventral surface of Chrysops vanderwulpi; C: The
head shot ofChrysops vanderwulpi;
D: The lateral side of Chrysops
dissectus's head; E: The wing of Chrysops vanderwulpi
图 2 土耳其麻虻形态图
A:土耳其麻虻背侧面;B:土耳其麻虻腹面;C:土耳其麻虻头部;
D:土耳其麻虻头部侧面;E:土耳其麻虻的翅
Fig. 2 Morphological map of Haematopota
turkestanica
A: The dorsal side of Haematopota
turkestanica; B: The ventral surface of Haematopota turkestanica; C:
The
head shot of Haematopota turkestanica;
D: The lateral side of Haematopota
turkestanica's head; E: The wing of Haematopota turkestanica
M: 2 000 DNA marker; 1: Chrysops vanderwulpi;2:
Haematopota turkestanica;
图 3 牛虻 cox 1 扩增结果图
Fig. 3 The cox 1 amplification results of gadflies
M:5 000 Marker CV-1:目的基因
图 4 范式斑虻 CV-1 基因序列 PCR 结果
Fig.4 The PCR results of the CV-1 gene
sequence of
C.vanderwulpi
M:5 000 Marker HT-1:目的基因
图 5 土耳其麻虻 HT-1 基因序列 PCR 结果
Fig.5 The PCR results of the HT-1 gene
sequence of
H.turkestanica
大创项目所依托课题组自 2011 年一直从事媒介节肢动物以及其传播病原的相关研究,已 发表相关的学术论文 50 余篇,其中一区论文 3 篇、二区论文 6 篇。获黑龙江省自然科学三等奖 1 项,授权发明专利 3 项,出版专著 2 部近年来,获批国家自然科学基金项目 2 项。在前期课题的资助下,项目主持人参与研究课题所撰写文章《Microbiota profile in organs of the Horsefly (Diptera: Tabanidae)in Northeastern China》投稿在 Science of the Total Environment。申请人请人已掌握虻种鉴定、肠 道菌群分离、生物信息学分析等技术,为本项目的顺利实施提供了坚实的技术保障。
| 开支科目 | 预算经费(元) | 主要用途 | 阶段下达经费计划(元) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 前半阶段 | 后半阶段 | |||
| 预算经费总额 | 20000.00 | 无 | 8200.00 | 11800.00 |
| 1. 业务费 | 16000.00 | 无 | 4700.00 | 11300.00 |
| (1)计算、分析、测试费 | 3500.00 | 购买辅助工具 | 2000.00 | 1500.00 |
| (2)能源动力费 | 0.00 | 无 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| (3)会议、差旅费 | 3000.00 | 交通、住宿费 | 1000.00 | 2000.00 |
| (4)文献检索费 | 3500.00 | 论文专利检索 | 1700.00 | 1800.00 |
| (5)论文出版费 | 6000.00 | 投稿论文 | 0.00 | 6000.00 |
| 2. 仪器设备购置费 | 1500.00 | 购买仪器、设备 | 1500.00 | 0.00 |
| 3. 实验装置试制费 | 1000.00 | 测试实验装置 | 1000.00 | 0.00 |
| 4. 材料费 | 1500.00 | 提供实验材料补给 | 1000.00 | 500.00 |